
- #Wifi scanner software install#
- #Wifi scanner software update#
- #Wifi scanner software driver#
- #Wifi scanner software full#
- #Wifi scanner software mac#
Thus, if you want to access it as a normal user, you have first to use visudo to set the SUDO program and then take help from the gksudo system. Type the following command: You can launch LinSSID in two ways as a root or as an ordinary user.
#Wifi scanner software install#
Ubuntu$ubuntu:~$ sudo apt install linssid -y

#Wifi scanner software update#
The next step is to update Ubuntu and then install LinSSID.Ubuntu$ubuntu:~$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:wseverin/ppa You can install LinSSID on your computer using PPA for DEB-based Linux distribution systems, including Linux Mint and Ubuntu.įollow these steps to install and run LinSSID on your device: What’s more? It has a graphical user interface that quickly detects all nearby WiFi routers and even ad-hoc connections. Moreover, as it is written in C++ with the help of Linux wireless tools, it provides an ideal performance on all sorts of systems. LinSSID is an easy-to-use Linux scanner that can scan both types of networks, 2.4GHz, and 5GHz. LinSSID – Graphical WiFi Networks Scanner Let’s take a look at the top 4 Linux WiFi Scanners. Using a Linux WiFi scanner lets you instantly figure out the optimal channel that comes within your WiFi network’s range. Top 4 Linux Scanners for Wireless Networks Wavemon – A ncurses-based Tool for Wireless Network Devices nmcli – A NetworkManager Controlling Tool

#Wifi scanner software full#
#Wifi scanner software driver#
Wireless network adapter and wireless card driver that works with the built-in wireless support of Windows Vista/7/8/.If you want to get wireless networks information on Windows XP, you can use the WirelessNetView utility. Windows XP is not supported because this tool is based on new Wi-Fi API that doesn't exist on Windows XP. Both 32-bit and 圆4 systems are supported. Operating System: This utility works on Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 7, and Windows Server 2008.Detection Count: The number of times that this network was detected.Last Detection: The last date/time that this network was detected.First Detection: The first date/time that this network was detected.Maximum Speed: The maximum speed (in Mbps) that you can get when connecting to this wireless network.Security: Specifies whether the network is secured (Yes/No).This value is displayed only for routers that provide this information inside the Wi-Fi information elements. Router Model: The model of the router.
#Wifi scanner software mac#
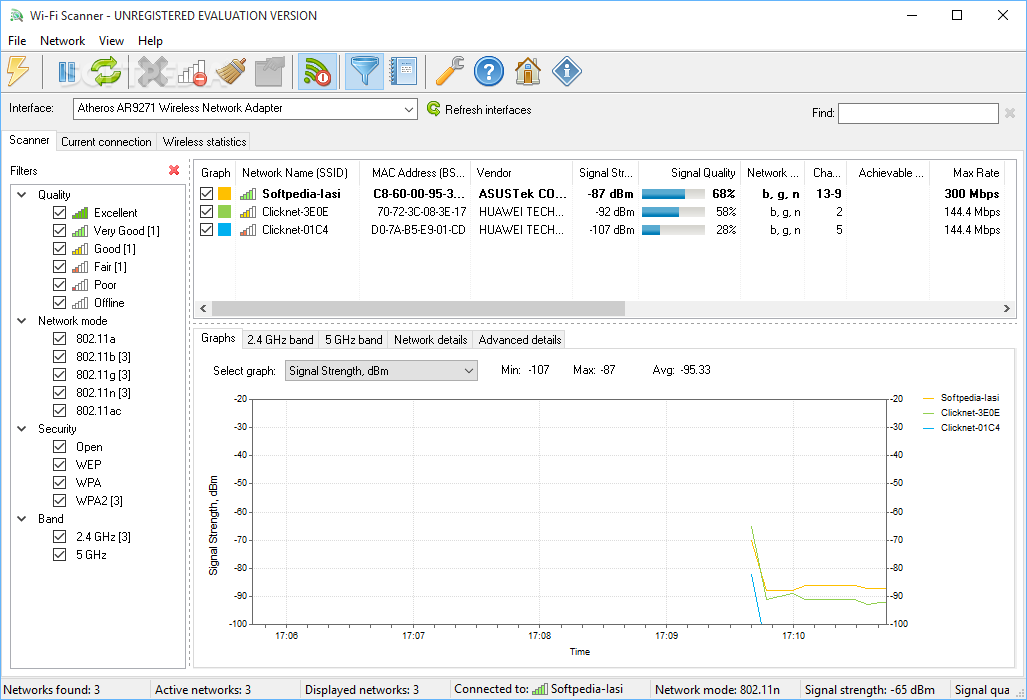
RSSI: The received signal strength indicator value, in units of decibels referenced to 1.0 milliwatts (dBm), as detected by the wireless LAN interface driver for the AP or peer station.PHY Type: The PHY type for this network - 802.11a, 802.11g, 802.11n, or High-Rate DSSS.MAC Address: MAC address of the router.When you select one or more wireless networks in the upper pane, the lower pane displays the Wi-Fi information elements of the selected items, in hexadecimal format. You can change update rate from Options->Update Rate menu. In order to start using it, simply run the executable file - WifiInfoView.exeĪfter you run WifiInfoView, the list of detected wireless networks in your area is displayed on the upper pane and it's updated at very high rate. WifiInfoView doesn't require any installation process or additional dll files. WifiInfoView also has a summary mode, which displays a summary of all detected wireless networks, grouped by channel number, company that manufactured the router, PHY type, or the maximum speed. When you select a wireless network in the upper pane of this tool, the lower pane displays the Wi-Fi information elements received from this device, in hexadecimal format. Including: Network Name (SSID), MAC Address, PHY Type (802.11g or 802.11n), RSSI, Signal Quality, Frequency, Channel Number, Maximum Speed, Company Name, Router Model and Router Name (Only for routers that provides this information), and more.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
